A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat from one place to another, in order to create a cooling action. It is used in a variety of situations, where heat transfer is required, such as in chemical plants, natural gas processing, and sewage treatment plants. It is also used in everyday machines and appliances, such as refrigerators and air conditioners. To gain a better understanding of the purpose of a heat exchanger, let's take a look how it works and what it is used for.
How does a heat exchanger work?
A heat exchanger works by transferring heat from one fluid (gas or liquid) to another, through the use of metal pipes and plates. Hot fluid flows from one side of a heat exchanger's metal partition, to the other side of the heat exchanger's partition, resulting in a reduction of temperature.
What is a heat exchanger made of?
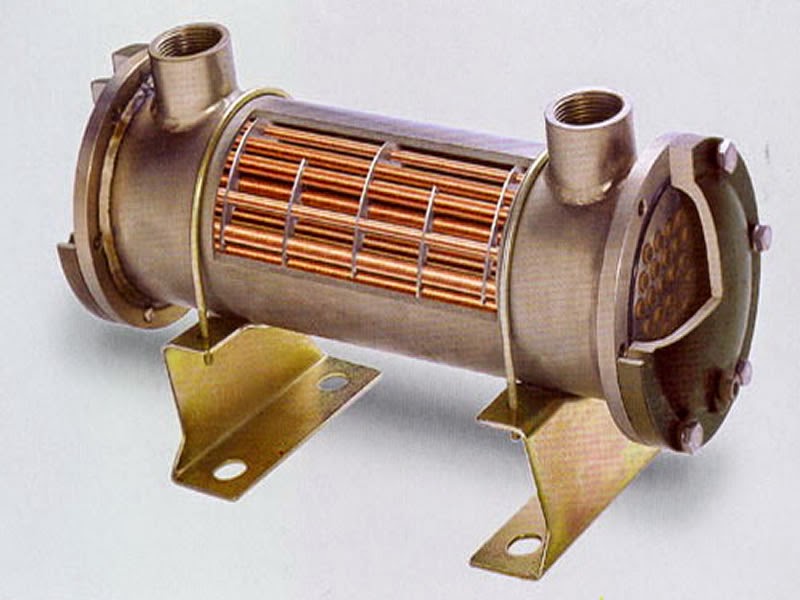
Heat exchangers are made in a variety of ways, for a variety of purposes, and in a variety of different sizes. Most commonly, a heat exchanger consists of coiled metal piping and metal plates. The coiled metal pipes contain fluid, which passes through a chamber containing another fluid, which cools down the fluid temperature. The most common material used for heat exchanger plates is stainless steel, due to its resistance to corrosion, strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. However, other metals such as copper, bronze, steel, aluminum and cast iron are sometimes used instead. The heat exchanger plates are spaced by sealing gaskets made from rubber, which are cemented into sections around the edge of the plates, which ensure the fluids do not touch or mix together. The combination of all these parts working together is what creates the cooling action on fluid.What are heat exchangers used for?
Heat exchangers are used in many machines and household appliances. Refrigerators and air conditions, for example, are common appliances that have heat exchangers built within them. A car radiator is also a heat exchanger. With a car radiator the exchanger transfers heat generated in the engine to the outside air, which keeps the engine cooled, preventing it from overheating. Heat exchangers are also used for transferring toxic substances, such as ethylene glycol (antifreeze).
One thing to note about heat exchangers is the importance of having them regularly checked. A cracked heat exchanger will leak carbon monoxide, which is poisonous to humans. Carbon monoxide is a gas; it has no scent, and cannot be seen or tasted. Undetected carbon monoxide can kill humans in as little as 10 minutes, and faulty heat exchangers are responsible for hundreds of deaths every year. In order to reduce the risk, have regular checkups on your appliances, and make sure each room of a building is fitted with a carbon monoxide detector.

No comments:
Post a Comment